In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, Blockchain Technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering unprecedented levels of security, transparency, and efficiency. But what exactly is blockchain, how does it work, and why is it crucial? In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its working mechanism, use cases, and its future potential.
What is Blockchain Technology?
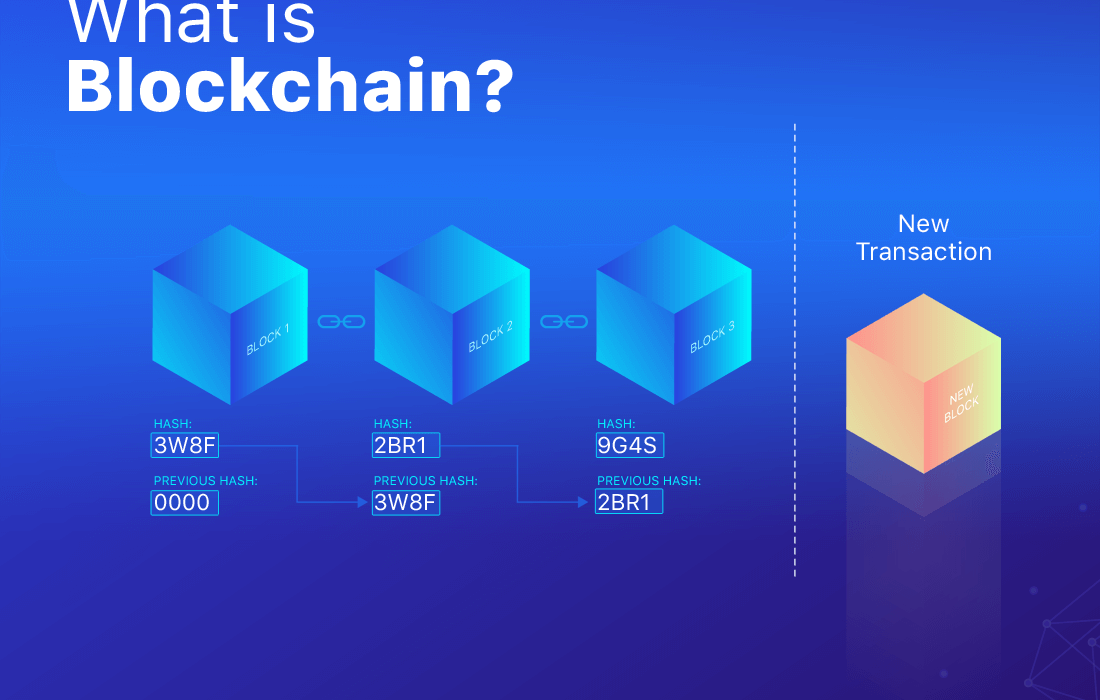
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that makes it nearly impossible to alter or hack. Each record in this ledger is called a block, and these blocks are connected using cryptographic principles, forming a chain.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Immutable Records: Once a block is added, it cannot be altered.
- Transparency: Transactions are visible to authorized participants.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain, enhancing trust.
- Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques make the system highly secure.
One prominent application of blockchain is Bitcoin, which uses this technology to secure its transactions. However, blockchain’s utility extends beyond cryptocurrencies, supporting applications in supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and more.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology relies on three core components:
- Cryptographic Keys: A pair of keys—Public Key and Private Key—ensures secure and verifiable transactions.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network: Enables decentralized and distributed data sharing among participants.
- Digital Ledger: Maintains transaction records across multiple nodes in the network.
The blockchain process begins when a transaction is initiated. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Step-by-Step Blockchain Process
- Initiation: A transaction is created and encrypted using the sender’s private key and the receiver’s public key.
- Block Creation: Transaction data is combined with a timestamp and digital signature to form a block.
- Verification: The block is broadcasted to the network nodes, where participants verify its authenticity.
- Addition to the Chain: Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain.
- Immutable Record: The transaction becomes part of an unalterable chain, ensuring transparency and security.
How Blockchain Handles Transactions
Blockchain transactions utilize cryptographic methods and distributed consensus to ensure security. Here’s a simplified example:
- Two Parties Involved: Person A wants to send money to Person B.
- Private and Public Keys: A uses their private key to encrypt transaction data and attaches it to B’s public key.
- Data Broadcast: The transaction is turned into a block and shared across the network for validation.
- Verification: Nodes in the network authenticate the transaction using cryptographic algorithms.
- Completion: Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain, completing the transaction.
Blockchain Use Cases
Blockchain technology is transforming industries by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions. Below are some notable use cases:
1. Hash Encryption for Security
- Blockchain employs SHA256 encryption to secure transaction details.
- Hash encryptions ensure that sensitive information remains protected while being verifiable by authorized participants.
2. Proof of Work
- Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism where miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions.
- Miners receive rewards for solving these puzzles, contributing to the blockchain’s security and functionality.
3. Mining Process
- Mining is the process of adding validated transaction blocks to the blockchain.
- Miners use computational power to solve nonce-hash combinations, ensuring the integrity of the chain.
Key Components of Blockchain
1. Blocks:
Each block contains:
- Previous Hash: Links to the prior block, maintaining the chain.
- Transaction Data: Details of transactions stored in the block.
- Nonce: A unique number used for solving the block’s hash.
- Hash: A cryptographic signature unique to the block.
2. Nodes:
Nodes are participants in the blockchain network that validate transactions and store copies of the blockchain.
3. Consensus Mechanisms:
These ensure agreement among nodes regarding the validity of transactions. Common methods include:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Enhanced Security: Data is encrypted and immutable.
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Efficiency: Faster processing of transactions.
- Transparency: Ensures accountability in systems like supply chains.
- Cost Savings: Reduces fees associated with traditional systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain offers numerous benefits, it also faces challenges:
- Scalability: Limited transaction processing speeds.
- Energy Consumption: Mining requires significant computational power.
- Regulatory Issues: Undefined legal frameworks in many jurisdictions.
- Adoption Barriers: Limited understanding and expertise in blockchain technology.
Future of Blockchain
The potential of blockchain is vast, with applications extending into voting systems, healthcare data management, real estate, and more. As industries recognize its value, blockchain is poised to become a cornerstone of technological innovation.
Example:
Bitcoin has already showcased blockchain’s power by revolutionizing financial transactions. Similarly, supply chain solutions powered by blockchain ensure transparency and reduce fraud.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology is reshaping the digital landscape by offering secure, transparent, and efficient ways to handle transactions and data. Whether through Bitcoin, supply chains, or healthcare, its applications are revolutionizing how we think about trust and decentralization.
By understanding the fundamentals of blockchain and its use cases, businesses and individuals can leverage this transformative technology to unlock new opportunities.
To learn more about the innovative startups shaping the future of the crypto industry, explore our article on latest news, where we delve into the most promising ventures and their potential to disrupt traditional industries.
Disclaimer: The information provided is not trading advice, Bitcoinworld.co.in holds no liability for any investments made based on the information provided on this page. We strongly recommend independent research and/or consultation with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions.